| [1]Yu SW, Yen CY, Wu CH, et al.Radiographic and clinical results of posterior dynamic stabilization for the treatment of multisegment degenerative disc disease with a minimum follow-up of 3 years.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2012; 132(5): 583-589.[2]Fay LY, Wu JC, Tsai TY, et al.Dynamic stabilization for degenerative spondylolisthesis: Evaluation of radiographic and clinical outcomes.Clin Neurol Neurosurg.2013; 115(5): 535-541.[3]缪德伟,卢建华.腰椎间盘突出症行磁共振成像的临床价值[J].浙江中医学院学报,2003,27(3):38-39.[4]刘先哲,杨闻,杨述华.腰椎非整合技术-Dynesys后路动态稳定系统临床应用研究[J].中国骨与关节外科,2009,2(2):165-167.[5]Schmoelz W, Huber JF, Nydegger T, et al.Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine and its effects on adjacent segments: an in vitro experiment.J Spinal Disord Tech.2003; 16(4):418-423.[6]蒋国强.腰椎后路Dynesys装置临床应用进展[J].现代实用医学, 2011,23(11):1203-1205.[7]Nockels RP.Dynamic stabilization in the surgical management of painful lumbar spinal disorders.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(16):S68-72.[8]Grob D, Benini A, Junge A, et al.Clinical experience with the Dynesys semirigid fixation system for the lumbar spine: surgical and patient-oriented outcome in 50 cases after an average of 2 years.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005; 30(3): 324-331.[9]Cunningham BW. Basic scientific considerations in total disc arthroplasty. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2004;4(6):219S-230S.[10]刘绮,马超,伍少玲,等.Oswestry功能障碍指数评定慢性腰痛患者的效度分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(3):228-231.[11]中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-1-12. https://www.cnki.net[12]万方数据库.万方数据知识服务平台[DB/OL].2013-1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn[13]张劲松.Dynesys动态稳定系统在腰椎退行性疾病中的应用及其与传统手术治疗方法的早期临床疗效比较[D].湖北:华中科技大学,2010:7-9. [14]李放,张志成,任大江.Dynesys动态稳定系统在腰椎退变性疾病治疗中的应用[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(5):288-292.[15]王孟.非融合技术与腰椎融合治疗腰椎退变性疾病的早期疗效观察[D].安徽:安徽医科大学,2012:5-7.[16]曹国永,杨渝勇,曹兴,等.Dynesys内固定系统治疗腰椎退变性疾病[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(12):1109-1111.[17]杨兵,江庭彪.动态中和系统与后路腰椎椎间融合治疗腰椎退行性变的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(2): 140-144. [18]李大伟,马远征,胡明,等.Bioflex动态稳定系统在多节段腰椎退行性疾病中的应用[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(4):286-289. [19]金政锡,元虎.Dynesys动态稳定系统在20例腰椎间盘突出症中的应用临床观察[J].延边大学医学学报,2012,35(4):289-291.[20]杨述华,许伟华,叶树楠,等.腰椎退行性疾病Dynesys动态固定早期临床观察[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2009,1(1):33-36. [21]Hoff E, Strube P, Rohlmann A, et al.Which radiographic parameters are linked to failure of a dynamic spinal implant?Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012 ;470(7):1834-1846.[22]Schwarzenbach O, Berlemann U, Stoll TM, et al.Posterior dynamic stabilization systems: DYNESYS.Orthop Clin North Am.2005;36(3):363-372.[23]Cabello J, Cavanilles-Walker JM, Iborra M, et al. The protective role of dynamic stabilization on the adjacent disc to a rigid instrumented level. An in vitro biomechanical analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2013;133(4):443-448. [24]Jahng TA, Kim YE, Moon KY.Comparison of the biomechanical effect of pedicle-based dynamic stabilization: a study using finite element analysis.Spine J.2013;13(1):85-94.[25]Shih SL, Chen CS, Lin HM, et al.Effect of spacer diameter of the Dynesys dynamic stabilization system on the biomechanics of the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis.J Spinal Disord Tech.2012;25(5):E140-149.[26]Kiapour A, Ambati D, Hoy RW, et al.Effect of graded facetectomy on biomechanics of Dynesys dynamic stabilization system.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2012;37(10): E581-589.[27]Lutz JA, Otten P, Maestretti G.Late infections after dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine with Dynesys.Eur Spine J. 2012;21(12):2573-2579.[28]Stoll TM, Dubois G, Schwarzenbach O.The dynamic neutralization system for the spine: a multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system.Eur Spine J. 2002;11 Suppl 2: S170-178.[29]Putzier M, Schneider SV, Funk JF, et al.The surgical treatment of the lumbar disc prolapse: nucleotomy with additional transpedicular dynamic stabilization versus nucleotomy alone.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(5): E109-114.[30]Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B.Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006; 31(4): 442-449.[31]Schaeren S, Broger I, Jeanneret B.Minimum four-year follow-up of spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and dynamic stabilization.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(18):E636-642.[32]Rahm MD, Hall BB.Adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion with instrumentation: a retrospective study.J Spinal Disord.1996;9(5):392-400.[33]Pellisé F, Hernández A, Vidal X, et al.Radiologic assessment of all unfused lumbar segments 7.5 years after instrumented posterior spinal fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(5): 574-579.[34]Beastall J, Karadimas E, Siddiqui M, et al.The Dynesys lumbar spinal stabilization system: a preliminary report on positional magnetic resonance imaging findings.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(6):685-690.[35]Kumar A, Beastall J, Hughes J, et al.Disc changes in the bridged and adjacent segments after Dynesys dynamic stabilization system after two years.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(26):2909-2914.[36]Cakir B, Carazzo C, Schmidt R, et al.Adjacent segment mobility after rigid and semirigid instrumentation of the lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(12):1287-1291 |
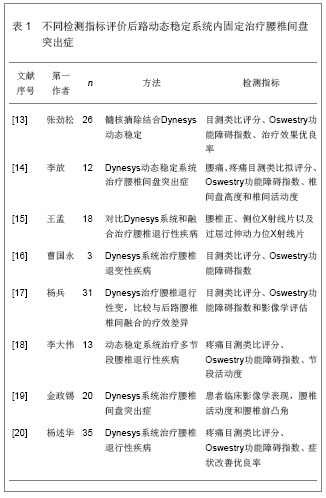
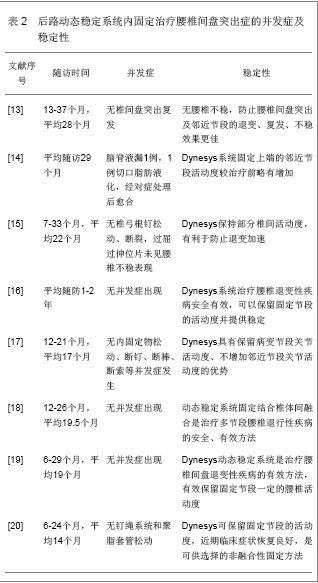
.jpg)